Chénopode rouge
(Chenopodium rubrum)

Une herbe annuelle de 30 à 80 cm de hauteur. La tige est dressée et rouge. Les feuilles sont en forme de triangle. Ils sont gros et ont des lobes émoussés. Il y a une enco ... (traduction automatique)
→suite
Chénopode rouge 

Note alimentaire ![]()
![]()
Une herbe annuelle de 30 à 80 cm de hauteur. La tige est dressée et rouge. Les feuilles sont en forme de triangle. Ils sont gros et ont des lobes émoussés. Il y a une encoche près de la pointe. Les fleurs sont des épis dressés (traduction automatique)
Pas d'autre illustration
pour le moment 😕
Classification
- Classique : en haut de l\'écran, sous le coeur.
- Phylogénétique :
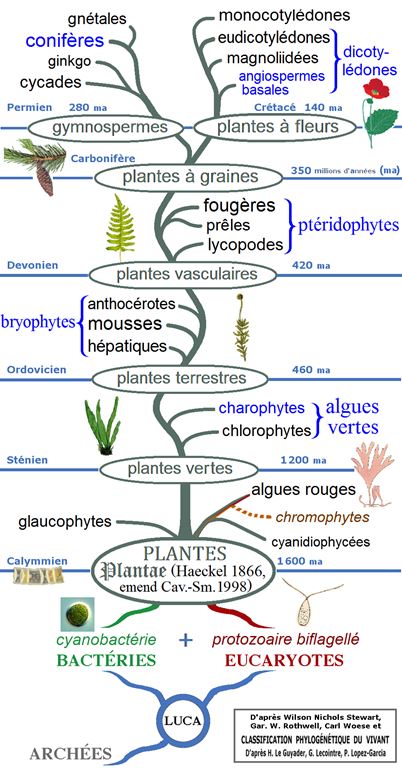
- Clade 4 : Angiospermes ;
- Clade 3 : Dicotylédones_vraies ;
- Ordre APN : Caryophyllales ;
- Famille APN : Amaranthaceae ;
Illustration : cet arbre phylogénétique des plantes montre les principaux clades et groupes traditionnels (monophylétiques en noir et paraphylétiques en bleu).
Dénominations
✖- Nom botanique : Chenopodium rubrum L. (1753)
- Synonymes : Agathophytum rubrum Rchb, Blitum acuminatum Schur, Blitum maritimum Nutt, Blitum polymorphum C. A. Mey, Blitum rubrum C. A, Mey, Blitum rubrum (L.) Reichenb, Botrys humilis (S. Watson) Lunell, Botrys rubra (L.) Lunell, Chenopodium astracanium Ledeb, Chenopodium blitoides Lej, Chenopodium humile Hook, Chenopodium matthioli Bertol. ex Moq, Chenopodium patulum Merat, Chenopodium pygaeum Menyh, et d'autres
- Noms anglais et locaux : pigweed, cenizo rojo (es)
Description et culture
✖- dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Description :
Une herbe annuelle de 30 à 80 cm de hauteur. La tige est dressée et rouge. Les feuilles sont en forme de triangle. Ils sont gros et ont des lobes émoussés. Il y a une encoche près de la pointe. Les fleurs sont des épis dressés{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : An annual herb 30-80 cm tall. The stem is erect and red. The leaves are triangle shaped. They are large and have blunt lobes. There is a notch near the tip. The flowers are erect spikes{{{0(+x).
Culture :
Les plantes sont cultivées à partir de graines{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : Plants are grown from seeds{{{0(+x).
 Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
✖
Ses feuilles sont comestibles{{{88. Feuilles cuites (ex. : comme potherbe) ? (qp*).(1*)
Partie testée :
/| Taux d'humidité | Énergie (kj) | Énergie (kcal) | Protéines (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| / | / | / | / |
| Pro- vitamines A (µg) |
Vitamines C (mg) | Fer (mg) | Zinc (mg) |
| / | / | / | / |
 Risques et précautions à prendre
Risques et précautions à prendre
✖
(1*)ATTENTION : cette plante peut accumuler des nitrates qui sont toxiques ; cela s'emplifie dans les sols riches en azote{{{0(+x). Présence de saponines et d'acide oxalique, pouvant être toxiques à fortes doses : voir fiches toxines, pour plus d'infos{{{(dp*).
Galerie(s)
✖
Par Sowerby J.E. (English Botany, or Coloured Figures of British Plants, 3th ed., vol. 8: t. 1197 ; 1868), via plantillustrations.org
Autres infos
✖dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Distribution :
C'est une plante tempérée. Il pousse sur des sites légèrement salés-alcalins, Il résiste à la sécheresse et au gel{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : It is a temperate plant. It grows on lightly salty-alkaline sites, It is resistant to drought and frost{{{0(+x).
Localisation :
Asie, Australie, Grande-Bretagne, Chine, Europe *, Irlande, Amérique du Nord, USA, Yougoslavie{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : Asia, Australia, Britain, China, Europe*, Ireland, North America, USA, Yugoslavia{{{0(+x).
Notes :
Il existe environ 100-150-250 espèces de Chenopodium. Ils se trouvent principalement dans les régions tempérées. Également mis dans la famille des Chenopodiaceae{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : There are about 100-150-250 Chenopodium species. They are mostly in temperate regions. Also put in the family Chenopodiaceae{{{0(+x).
Liens, sources et/ou références
✖Sources et/ou références :
Tela Botanica ; FloreAlpes ; HYPPA ; Wikipedia ; Wikipedia (en allemand) ; Wikipedia (en anglais) ; 5"Plants For A Future" (en anglais) ;
dont classification : "The Plant List" (en anglais) ;
dont livres et bases de données : 88Sauvages et comestibles (livre, page 94, par Marie-Claude Paume) ;
Sauvages & comestibles - herbes, fleurs et petites salades (de Marie-Claude Paume, éditions EDISUB, 2011) / détails du livre
Recherche de/pour :
- "Chenopodium rubrum" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
INPI (en anglais) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
- "Chénopode rouge" sur Google (pages, images et recettes) ;
- "Chenopodium rubrum" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
INPI (en anglais) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
Espèces du même genre (Chenopodium)
✖50 taxons
- Chenopodium acuminatum
- Chenopodium album L. (Chénopode blanc)
- Chenopodium auricomum Lindl. (Épinard d'Australie)
- Chenopodium berlandieri (Chénopode de Berlandier)
- Chenopodium bonus-henricus L. (Chénopode bon Henri)
- Chenopodium botrys
- Chenopodium bryoniifolium
- Chenopodium bushianum
- Chenopodium californicum
- Chenopodium canihua
- Chenopodium capitatum (L.) Asch. (Épinard fraise)
- Chenopodium carnosulum
- Chenopodium chenopodioides
- Chenopodium cornutum
- Chenopodium cristatum
- Chenopodium erosum
- Chenopodium ficifolium Sm. (Chénopode tardif)
- Chenopodium foliosum (Moench) Asch. (Épinard-fraise)
- Chenopodium formosanum
- Chenopodium fremontii
- Chenopodium giganteum D.Don (Épinard arbre)
- Chenopodium glaucum L. (Chénopode glauque)
- Chenopodium graveolens
- Chenopodium hircinum
- Chenopodium hybridum L. (Ansérine hybride)
- Chenopodium incanum
- Chenopodium incisum
- Chenopodium leptophyllum
- Chenopodium murale L. (Chénopode des murs)
- Chenopodium nitrariaceum
- Chenopodium nuttalliae Saff. (Huauzontle)
- Chenopodium oahense
- Chenopodium opulifolium
- Chenopodium overi
- Chenopodium pallidicaule Aellen (Canihua)
- Chenopodium petiolare
- Chenopodium polyspermum L. (Chénopode à graines nombreuses)
- Chenopodium pratericola
- Chenopodium quinoa Willd. (Quinoa)
- Chenopodium rubrum L. (Chénopode rouge)
- Chenopodium schraderianum
- Chenopodium serotinum
- Chenopodium simplex
- Chenopodium sosnowskyi
- Chenopodium stenophyllum
- Chenopodium suecicum
- Chenopodium urbicum L. (Ansérine des villages)
- Chenopodium virgatum
- Chenopodium viride
- Chenopodium vulvaria L. (Chénopode fétide)
Espèces de la même famille (Amaranthaceae)
✖50 taxons (sur 358)
- Achyranthes aspera L.
- Achyranthes bidentata Blume (Ox-knee)
- Achyranthes faureri
- Achyranthes japonica
- Acroglochin persicarioides
- Aerva javanica
- Aerva lanata
- Aerva leucura
- Aerva sanguinolenta
- Aerva tomentosa
- Agriophyllum squarrosum (L.) Moq. (Soulkhir)
- Allenrolfea occidentalis
- Allmania nodiflora
- Alternanthera bettzickiana
- Alternanthera brasiliana
- Alternanthera denticulata
- Alternanthera echinata
- Alternanthera ficoidea
- Alternanthera littoralis
- Alternanthera nodiflora
- Alternanthera paronychioides
- Alternanthera philoxeroides
- Alternanthera pungens
- Alternanthera sessilis (L.) DC. (Alternante sessile)
- Alternanthera sissoo Hort. (Epinard bresilien)
- Alternanthera versicolor
- Amaranthus acanthochiton Sauer
- Amaranthus albus L. (Amaranthe blanche)
- Amaranthus angustifolius
- Amaranthus arenicola
- Amaranthus atropurpureus
- Amaranthus australis (A.Gray) Sauer
- Amaranthus bidentata
- Amaranthus blitoides
- Amaranthus blitum L. (Amaranthe blette)
- Amaranthus campestris
- Amaranthus caudatus L. (Amaranthe caudée)
- Amaranthus chirotarota
- Amaranthus crassipes
- Amaranthus cruentus L. (Amaranthe étalée)
- Amaranthus deflexus L. (Amarante couchée)
- Amaranthus diacanthus
- Amaranthus dubius Mart. ex Thell. (Amaranthe épinard)
- Amaranthus fimbriatus
- Amaranthus frumentaceus
- Amaranthus giganteus
- Amaranthus gracilis
- Amaranthus graecizans L. (Amaranthe africaine)
- Amaranthus grandiflorus
- Amaranthus hybridus L. (Amaranthe hybride)
- ...