Caryer à gros bourgeons
(Carya tomentosa)

Un grand arbre. Il atteint 30 m de haut. L'écorce est gris foncé et présente des crêtes plates et des sillons peu profonds. L'arbre a une couronne arrondie. Les feuilles s ... (traduction automatique)
→suite
Caryer à gros bourgeons 
Note alimentaire ![]()
![]()
![]()
Note médicinale ![]()
Un grand arbre. Il atteint 30 m de haut. L'écorce est gris foncé et présente des crêtes plates et des sillons peu profonds. L'arbre a une couronne arrondie. Les feuilles sont composées et mesurent 20 à 50 cm de long. Les feuilles ont 9 folioles oblongues. Elles sont vert foncé sur la face supérieure et duveteus... (traduction automatique) →suite
Pas d'autre illustration
pour le moment 😕
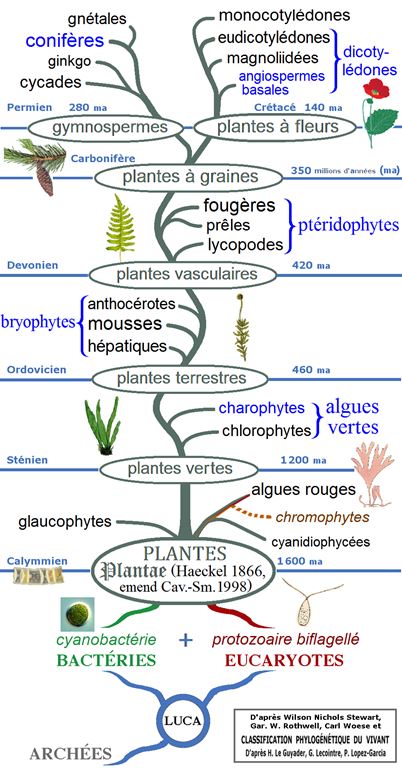
Classification
- Classique : en haut de l\'écran, sous le coeur.
- Phylogénétique :
- Clade 4 : Angiospermes ;
- Clade 3 : Dicotylédones_vraies ;
- Clade 2 : Rosidées ;
- Clade 1 : Fabidées ;
- Ordre APN : Fagales ;
- Famille APN : Juglandaceae ;
Illustration : cet arbre phylogénétique des plantes montre les principaux clades et groupes traditionnels (monophylétiques en noir et paraphylétiques en bleu).
Dénominations
✖- Nom botanique : Carya tomentosa (Poir.) Nutt. (1818)
- Synonymes français : caryer moqueur
- Synonymes : Carya alba (L.) Nutt. 1818 (synonyme selon GRIN ; nom accepté et "synonyme de" {nom retenu}, selon TPL), Carya alba (L.) Nutt. ex Elliott. 1818 (synonyme selon GRIN ; nom accepté et "synonyme de" {nom retenu}, selon TPL), Juglans tomentosa Michx. 1803 ;
- Noms anglais et locaux : mockernut hickory, bullnut, white hickory, square nut
Description et culture
✖- dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Description :
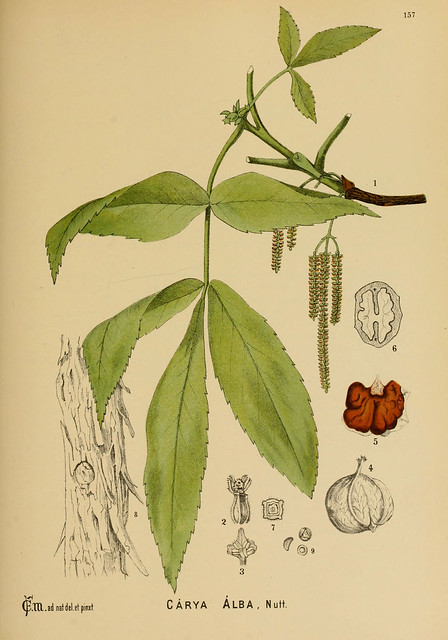
Un grand arbre. Il atteint 30 m de haut. L'écorce est gris foncé et présente des crêtes plates et des sillons peu profonds. L'arbre a une couronne arrondie. Les feuilles sont composées et mesurent 20 à 50 cm de long. Les feuilles ont 9 folioles oblongues. Elles sont vert foncé sur la face supérieure et duveteuses en dessous. Les fleurs sont très petites et vertes. Les fleurs mâles sont en minces chatons tombants. Il y a 3 chatons suspendus à une tige. Il y a 2 à 5 fleurs femelles à l'extrémité de la même brindille. La coque du fruit est épaisse. Les fruits sont ronds à ovales et mesurent 35 mm de diamètre. Les noix sont comestibles{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : A large tree. It grows 30 m tall. The bark is dark grey and has flat ridges and shallow furrows. The tree has a rounded crown. The leaves are compound and 20-50 cm long. The leaves have 9 oblong leaflets They are dark green on the upper surface and downy underneath. The flowers are very small and green. The male flowers are in slender drooping catkins. There are 3 catkins hanging from one stalk. There are 2-5 female flowers at the tip of the same twig. The shell of the fruit is thick. The fruit are round to oval and 35 mm across. The nuts are edible{{{0(+x).
Production :
Les coquilles sont difficiles à casser{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : The shells are hard to crack{{{0(+x).
Culture :
Les plantes sont cultivées à partir de graines. Il peut également être cultivé par boutures{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : Plants are grown from seeds. It can also be grown by cuttings{{{0(+x).
 Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
✖
Fruit (graines {noix}{{{0(+x) [nourriture/aliment, garniture et/ou assaisonnement{{{(dp*) et tronc (extrait(dp*) {sève0(+x)} [base boissons/breuvages{{{(dp*)]) comestibles0(+x).
Partie testée :
noix{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique). Original : Nuts{{{0(+x)| Taux d'humidité | Énergie (kj) | Énergie (kcal) | Protéines (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| / | / | / | / |
| Pro- vitamines A (µg) |
Vitamines C (mg) | Fer (mg) | Zinc (mg) |
| / | / | / | / |
 Risques et précautions à prendre
Risques et précautions à prendre
✖
néant, inconnus ou indéterminés.
Galerie(s)
✖
BioDivLibrary, via flickr
Autres infos
✖dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Distribution :
C'est une plante tempérée. Il pousse sur des collines plus sèches aux États-Unis. Il pousse jusqu'à 900 m d'altitude. Il convient aux zones de rusticité 4-9{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : It is a temperate plant. It grows on drier hills in the USA. It grows up to 900 m altitude. It suits hardiness zones 4-9{{{0(+x).
Localisation :
Australie, Grande-Bretagne, Canada, Allemagne, Amérique du Nord, USA{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : Australia, Britain, Canada, Germany, North America, USA{{{0(+x).
Notes :
Il existe environ 14 à 25 espèces de Carya{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : There are about 14-25 Carya species{{{0(+x).
Liens, sources et/ou références
✖Sources et/ou références :
dont classification : "The Plant List" (en anglais) ; "GRIN" (en anglais) ;
dont livres et bases de données : 0"Food Plants International" (en anglais) ;
dont biographie/références de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Bircher, A. G. & Bircher, W. H., 2000, Encyclopedia of Fruit Trees and Edible Flowering Plants in Egypt and the Subtropics. AUC Press. p 87 ; Bodkin, F., 1991, Encyclopedia Botanica. Cornstalk publishing, p 219 ; Brouk, B., 1975, Plants Consumed by Man. Academic Press, London. p 221 ; Duke, J.A., 1992, Handbook of Edible Weeds. CRC Press. p 62 ; Elias, T.S. & Dykeman P.A., 1990, Edible Wild Plants. A North American Field guide. Sterling, New York p 244 ; Esperanca, M. J., 1988. Surviving in the wild. A glance at the wild plants and their uses. Vol. 2. p 90 ; Etherington, K., & Imwold, D., (Eds), 2001, Botanica's Trees & Shrubs. The illustrated A-Z of over 8500 trees and shrubs. Random House, Australia. p 185 ; Facciola, S., 1998, Cornucopia 2: a Source Book of Edible Plants. Kampong Publications, p 123 ; Flowerdew, B., 2000, Complete Fruit Book. Kyle Cathie Ltd., London. p 194 ; Gen. N. Amer. pl. 2:221. 1818 ; Glowinski, L., 1999, The Complete Book of Fruit Growing in Australia. Lothian. p 106 ; Gouldstone, S., 1983, Growing your own Food-bearing Plants in Australia. Macmillan p 144 ; Grandtner, M. M., 2008, World Dictionary of Trees. Wood and Forest Science Department. Laval University, Quebec, Qc Canada. (Internet database https://www.WDT.QC.ca) ; Hedrick, U.P., 1919, (Ed.), Sturtevant's edible plants of the world. p 172 ; Little, E.L., 1980, National Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Trees. Alfred A. Knopf. p 355 ; Lyle, S., 2006, Discovering fruit and nuts. Land Links. p 112 ; Menninger, E.A., 1977, Edible Nuts of the World. Horticultural Books. Florida p 5 ; Plants For A Future database, The Field, Penpol, Lostwithiel, Cornwall, PL22 0NG, UK. https://www.scs.leeds.ac.uk/pfaf/ ; Wickens, G.E., 1995, Edible Nuts. FAO Non-wood forest products. FAO, Rome. p 134
Recherche de/pour :
- "Carya tomentosa" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
- "Caryer à gros bourgeons" sur Google (pages, images et recettes) ;
- "Carya tomentosa" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
Espèces du même genre (Carya)
✖25 taxons
- Carya aquatica (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Pacanier amer)
- Carya buckleyi
- Carya californica
- Carya carolinae-septentrionalis
- Carya cathayensis Sarg. (Caryer de cathay)
- Carya cordiformis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Caryer cordiforme)
- Carya floridana Sarg.
- Carya glabra (Mill.) Sweet. (Caryer à noix porcines)
- Carya hunanensis
- Carya hybrids
- Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Pacanier)
- Carya laciniosa (F.Michx.) Loudon. (Noyer roi)
- Carya myristiciformis (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Nogal)
- Carya ovalis (Wangenh.) Sarg.
- Carya ovata (Mill.) K.Koch. (Caryer ovale)
- Carya pallida (Ashe.) Engelm. & Graebn.
- Carya poilanei
- Carya sinensis
- Carya texana Buckley.
- Carya tomentosa (Poir.) Nutt. (Caryer à gros bourgeons)
- Carya tonkinensis
- Carya x brownii
- Carya x laneyi Sarg.
- Carya x laneyi
- Carya x nussbaumeri
Espèces de la même famille (Juglandaceae)
✖50 taxons (sur 61)
- Carya aquatica (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Pacanier amer)
- Carya buckleyi
- Carya californica
- Carya carolinae-septentrionalis
- Carya cathayensis Sarg. (Caryer de cathay)
- Carya cordiformis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Caryer cordiforme)
- Carya floridana Sarg.
- Carya glabra (Mill.) Sweet. (Caryer à noix porcines)
- Carya hunanensis
- Carya hybrids
- Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Pacanier)
- Carya laciniosa (F.Michx.) Loudon. (Noyer roi)
- Carya myristiciformis (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Nogal)
- Carya ovalis (Wangenh.) Sarg.
- Carya ovata (Mill.) K.Koch. (Caryer ovale)
- Carya pallida (Ashe.) Engelm. & Graebn.
- Carya poilanei
- Carya sinensis
- Carya texana Buckley.
- Carya tomentosa (Poir.) Nutt. (Caryer à gros bourgeons)
- Carya tonkinensis
- Carya x brownii
- Carya x laneyi Sarg.
- Carya x laneyi
- Carya x nussbaumeri
- Cathya cathayensis
- Cyclocarya paliurus
- Engelhardtia serrata
- Engelhardtia spicata
- Juglans ailanthifolia Carrière (Noyer japonais)
- Juglans australis
- Juglans boliviana
- Juglans californica
- Juglans cathayensis
- Juglans cinerea L. (Noyer cendré)
- Juglans hindsii
- Juglans hirsuta
- Juglans honorei
- Juglans intermedia
- Juglans jamaicensis
- Juglans major (Torr.) A. Heller (Noyer noir d'arizona)
- Juglans mandschurica
- Juglans mexicana
- Juglans microcarpa Berland. (Noyer du texas)
- Juglans mollis
- Juglans neotropica Diels (Noyer noir)
- Juglans nigra L. (Noyer d'amérique)
- Juglans olanchana
- Juglans regia L. (Noyer commun)
- Juglans sigillata
- ...