Carya pallida
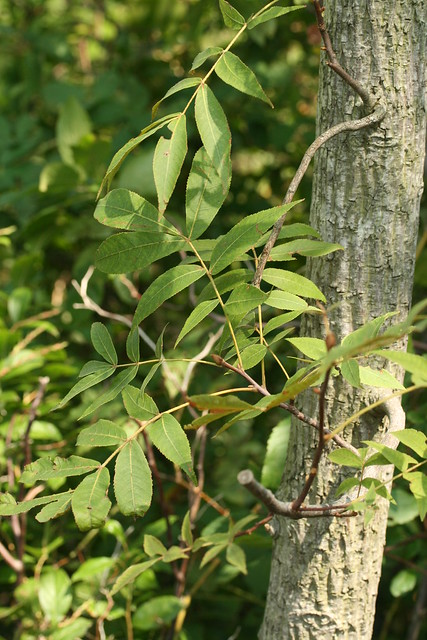

Un grand arbre. Il atteint 24 m de haut. Le tronc mesure 30 à 60 cm de diamètre. L'écorce est lisse et présente de profondes rainures. Les feuilles sont composées et mesu ... (traduction automatique)
→suite
Carya pallida 
Note alimentaire ![]()
![]()
![]()
Note médicinale ![]()
Un grand arbre. Il atteint 24 m de haut. Le tronc mesure 30 à 60 cm de diamètre. L'écorce est lisse et présente de profondes rainures. Les feuilles sont composées et mesurent 18 à 38 cm de long. Les feuilles ont 7 à 9 folioles le long de la tige. Ils sont vert clair au-dessus et ont des écailles gris argenté e... (traduction automatique) →suite
Pas d'autre illustration
pour le moment 😕
Classification
- Classique : en haut de l\'écran, sous le coeur.
- Phylogénétique :
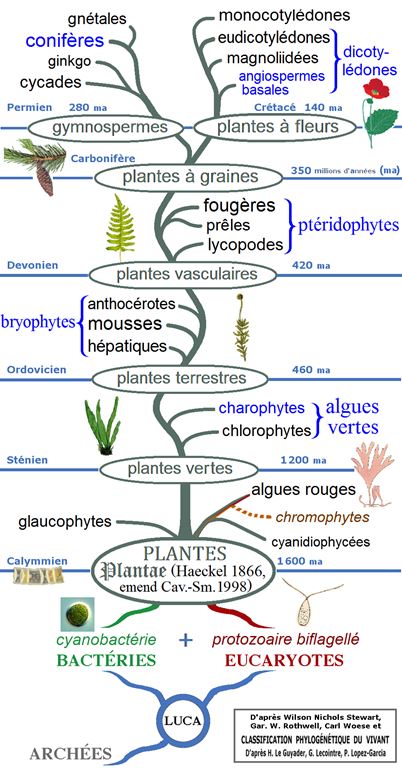
- Clade 4 : Angiospermes ;
- Clade 3 : Dicotylédones_vraies ;
- Clade 2 : Rosidées ;
- Clade 1 : Fabidées ;
- Ordre APN : Fagales ;
- Famille APN : Juglandaceae ;
Illustration : cet arbre phylogénétique des plantes montre les principaux clades et groupes traditionnels (monophylétiques en noir et paraphylétiques en bleu).
Dénominations
✖- Nom botanique : Carya pallida (Ashe.) Engelm. & Graebn. (1902)
- Synonymes : Hicoria pallida
- Noms anglais et locaux : sand hickory, pale leaf hickory
Description et culture
✖- dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Description :
Un grand arbre. Il atteint 24 m de haut. Le tronc mesure 30 à 60 cm de diamètre. L'écorce est lisse et présente de profondes rainures. Les feuilles sont composées et mesurent 18 à 38 cm de long. Les feuilles ont 7 à 9 folioles le long de la tige. Ils sont vert clair au-dessus et ont des écailles gris argenté en dessous. Les fleurs sont très petites et verdâtres. Les fleurs mâles sont en minces chatons tombants. Il y a 3 fleurs suspendues à une tige. Les fleurs femelles se produisent séparément à l'extrémité de la même brindille. Le fruit est ovale et long de 30 mm. Il se fend à la base à maturité. La graine est comestible{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : A large tree. It grows 24 m high. The trunk is 30-60 cm across. The bark is smooth and has deep grooves. The leaves are compound and 18-38 cm long. The leaves have 7-9 leaflets along the stalk. They are light green above and have silver-grey scales underneath. The flowers are very small and greenish. The male flowers are in slender drooping catkins. There are 3 flowers hanging from one stalk. The female flowers occur singly at the tip of the same twig. The fruit is oval and 30 mm long. It splits at the base when ripe. The seed is edible{{{0(+x).
 Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
✖
Fruit (graines {noix}{{{0(+x) [nourriture/aliment, garniture et/ou assaisonnement{{{(dp*) comestible0(+x).
Partie testée :
noix{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique). Original : Nuts{{{0(+x)| Taux d'humidité | Énergie (kj) | Énergie (kcal) | Protéines (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| / | / | / | / |
| Pro- vitamines A (µg) |
Vitamines C (mg) | Fer (mg) | Zinc (mg) |
| / | / | / | / |
 Risques et précautions à prendre
Risques et précautions à prendre
✖
néant, inconnus ou indéterminés.
Galerie(s)
✖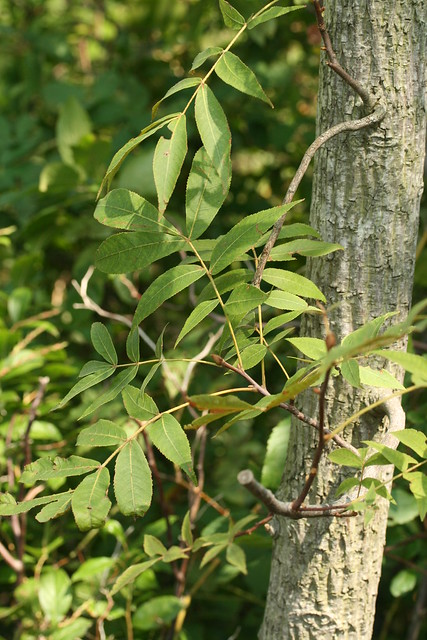
Par dogtooth77, via flickr
Autres infos
✖dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Distribution :
Il pousse sur des sols sableux et rocheux secs. Il pousse à 760 m d'altitude aux USA. Il convient aux zones de rusticité 6-9{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : It grows on dry sandy and rocky soils. It grows to 760 m altitude in the USA. It suits hardiness zones 6-9{{{0(+x).
Localisation :
Grande-Bretagne, Amérique du Nord, USA{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : Britain, North America, USA{{{0(+x).
Notes :
Il existe environ 14 à 25 espèces de Carya{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : There are about 14-25 Carya species{{{0(+x).
Liens, sources et/ou références
✖Sources et/ou références :
dont classification : "The Plant List" (en anglais) ; "GRIN" (en anglais) ;
dont livres et bases de données : 0"Food Plants International" (en anglais) ;
dont biographie/références de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Bircher, A. G. & Bircher, W. H., 2000, Encyclopedia of Fruit Trees and Edible Flowering Plants in Egypt and the Subtropics. AUC Press. p 87 ; H. G. A. Engler, Notizbl. Koenigl. Bot. Gart. Berlin App. 9:19. 1902 ; Etherington, K., & Imwold, D., (Eds), 2001, Botanica's Trees & Shrubs. The illustrated A-Z of over 8500 trees and shrubs. Random House, Australia. p 185 ; Little, E.L., 1980, National Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Trees. Alfred A. Knopf. p 353 ; Plants For A Future database, The Field, Penpol, Lostwithiel, Cornwall, PL22 0NG, UK. https://www.scs.leeds.ac.uk/pfaf/ ; Wickens, G.E., 1995, Edible Nuts. FAO Non-wood forest products. FAO, Rome. p 134
Recherche de/pour :
- "Carya pallida" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
- "Carya pallida" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
Espèces du même genre (Carya)
✖25 taxons
- Carya aquatica (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Pacanier amer)
- Carya buckleyi
- Carya californica
- Carya carolinae-septentrionalis
- Carya cathayensis Sarg. (Caryer de cathay)
- Carya cordiformis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Caryer cordiforme)
- Carya floridana Sarg.
- Carya glabra (Mill.) Sweet. (Caryer à noix porcines)
- Carya hunanensis
- Carya hybrids
- Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Pacanier)
- Carya laciniosa (F.Michx.) Loudon. (Noyer roi)
- Carya myristiciformis (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Nogal)
- Carya ovalis (Wangenh.) Sarg.
- Carya ovata (Mill.) K.Koch. (Caryer ovale)
- Carya pallida (Ashe.) Engelm. & Graebn.
- Carya poilanei
- Carya sinensis
- Carya texana Buckley.
- Carya tomentosa (Poir.) Nutt. (Caryer à gros bourgeons)
- Carya tonkinensis
- Carya x brownii
- Carya x laneyi Sarg.
- Carya x laneyi
- Carya x nussbaumeri
Espèces de la même famille (Juglandaceae)
✖50 taxons (sur 61)
- Carya aquatica (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Pacanier amer)
- Carya buckleyi
- Carya californica
- Carya carolinae-septentrionalis
- Carya cathayensis Sarg. (Caryer de cathay)
- Carya cordiformis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Caryer cordiforme)
- Carya floridana Sarg.
- Carya glabra (Mill.) Sweet. (Caryer à noix porcines)
- Carya hunanensis
- Carya hybrids
- Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch. (Pacanier)
- Carya laciniosa (F.Michx.) Loudon. (Noyer roi)
- Carya myristiciformis (F.Michx.) Nutt. (Nogal)
- Carya ovalis (Wangenh.) Sarg.
- Carya ovata (Mill.) K.Koch. (Caryer ovale)
- Carya pallida (Ashe.) Engelm. & Graebn.
- Carya poilanei
- Carya sinensis
- Carya texana Buckley.
- Carya tomentosa (Poir.) Nutt. (Caryer à gros bourgeons)
- Carya tonkinensis
- Carya x brownii
- Carya x laneyi Sarg.
- Carya x laneyi
- Carya x nussbaumeri
- Cathya cathayensis
- Cyclocarya paliurus
- Engelhardtia serrata
- Engelhardtia spicata
- Juglans ailanthifolia Carrière (Noyer japonais)
- Juglans australis
- Juglans boliviana
- Juglans californica
- Juglans cathayensis
- Juglans cinerea L. (Noyer cendré)
- Juglans hindsii
- Juglans hirsuta
- Juglans honorei
- Juglans intermedia
- Juglans jamaicensis
- Juglans major (Torr.) A. Heller (Noyer noir d'arizona)
- Juglans mandschurica
- Juglans mexicana
- Juglans microcarpa Berland. (Noyer du texas)
- Juglans mollis
- Juglans neotropica Diels (Noyer noir)
- Juglans nigra L. (Noyer d'amérique)
- Juglans olanchana
- Juglans regia L. (Noyer commun)
- Juglans sigillata
- ...