Pomme noire
(Planchonella australis)
Un grand arbre. Il atteint 15-25 m de haut. Les feuilles sont d'un vert foncé brillant. Les fleurs sont petites et blanches. Les fruits sont gros et noirs (traduction automatique)
→suite
Pomme noire 
Note alimentaire ![]()
![]()
![]()
Un grand arbre. Il atteint 15-25 m de haut. Les feuilles sont d'un vert foncé brillant. Les fleurs sont petites et blanches. Les fruits sont gros et noirs (traduction automatique)
Pas d'autre illustration
pour le moment 😕
Classification
- Classique : en haut de l\'écran, sous le coeur.
- Phylogénétique :
- Clade 4 : Angiospermes ;
- Clade 3 : Dicotylédones_vraies ;
- Clade 2 : Astéridées ;
- Ordre APN : Ericales ;
- Famille APN : Sapotaceae ;
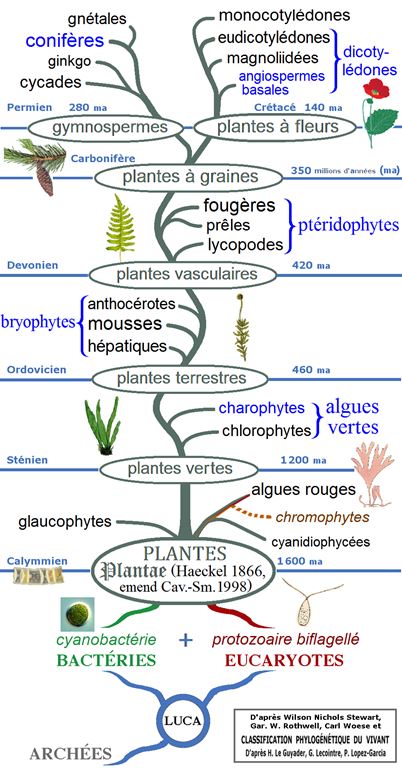
Illustration : cet arbre phylogénétique des plantes montre les principaux clades et groupes traditionnels (monophylétiques en noir et paraphylétiques en bleu).
Dénominations
✖- Nom botanique : Planchonella australis (R.Br.) Pierre (1890)
- Synonymes français : prune noire
- Synonymes : Pouteria australis (R.Br.) Baehni 1942 ;
- Noms anglais et locaux : black apple (black-apple), black-plum, wild plum, yellow buttonwood, yellow bulletwood
Description et culture
✖- dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Description :
Un grand arbre. Il atteint 15-25 m de haut. Les feuilles sont d'un vert foncé brillant. Les fleurs sont petites et blanches. Les fruits sont gros et noirs{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : A large tree. It grows 15-25 m high. The leaves are a dark shiny green. The flower are small and white. The fruit are large and black{{{0(+x).
 Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
Consommation (rapports de comestibilité, parties utilisables et usages alimentaires correspondants)
✖
Partie(s) comestible(s){{{0(+x) : fruit0(+x).
Utilisation(s)/usage(s){{{0(+x) culinaire(s) : les fruits sont utilisés pour faire de la confiture{{{0(+x).
Partie testée :
fruit{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique). Original : Fruit{{{0(+x)| Taux d'humidité | Énergie (kj) | Énergie (kcal) | Protéines (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 74.7 | 213 | 51 | 2.2 |
| Pro- vitamines A (µg) |
Vitamines C (mg) | Fer (mg) | Zinc (mg) |
| / | 5 | 1.0 | 0.3 |
 Risques et précautions à prendre
Risques et précautions à prendre
✖
néant, inconnus ou indéterminés.
Galerie(s)
✖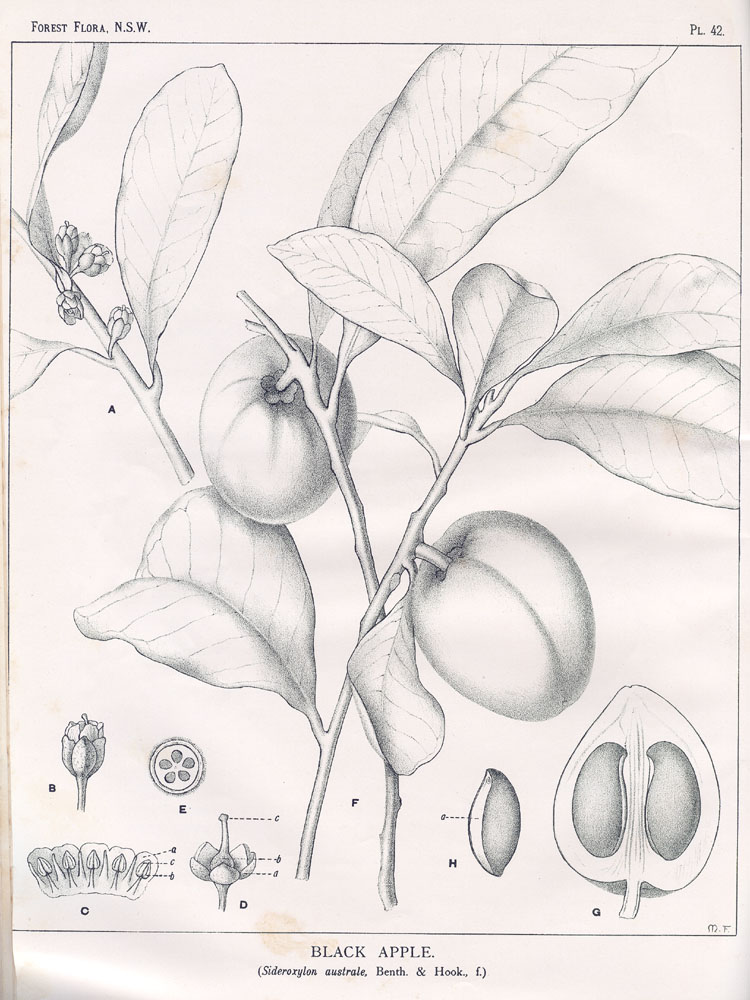
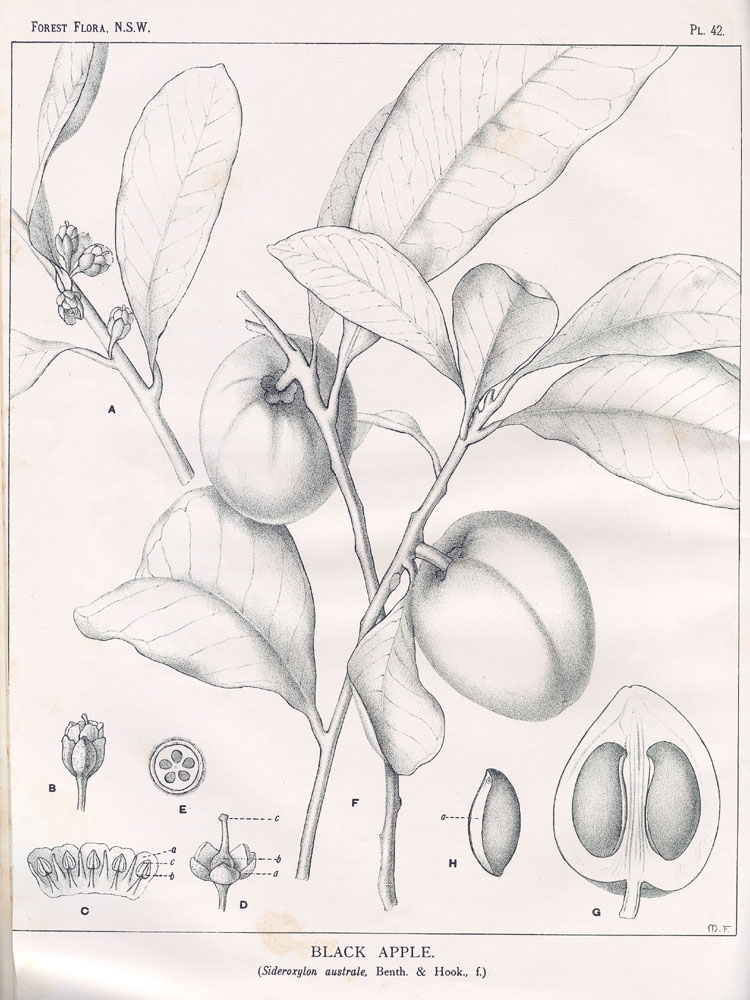
Par Maiden, J.H., Forest Flora of New South Wales (1904-1925) Forest Fl. N.S.W. vol. 2 (1904) t. 42, via plantillustrations
Autres infos
✖dont infos de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Statut :
Les fruits sont comestibles mais pas savoureux{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : The fruit are edible but not tasty{{{0(+x).
Distribution :
C'est une plante subtropicale. Il est préférable en position humide et semi-ombragée. Il a besoin d'un abri contre les vents forts{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : It is a subtropical plant. It is best in moist, semi-shaded position. It needs shelter from strong winds{{{0(+x).
Localisation :
Australie*{{{0(+x) (traduction automatique).
Original : Australia*{{{0(+x).
Liens, sources et/ou références
✖Sources et/ou références :
5"Plants For A Future" (en anglais) ;
dont classification : "The Plant List" (en anglais) ; "GRIN" (en anglais) ;
dont livres et bases de données : 0"Food Plants International" ([Pouteria australis (R.Br.) Baehni], en anglais) ;
dont biographie/références de "FOOD PLANTS INTERNATIONAL" :
Anon., 2003, Native Plants for the Fitzroy basin. Society for Growing Australian Plants Inc. (Rockhampton Branch) p 73 ; Barwick, M., 2004, Tropical and Subtropical Trees. A Worldwide Encyclopedic Guide. Thames and Hudson p 344 (As Planchonella australis) ; Bodkin, F., 1991, Encyclopedia Botanica. Cornstalk publishing, p 808 (As Planchonella australis) ; Candollea 9:308. 1942 ; Cherikoff V. & Isaacs, J., The Bush Food Handbook. How to gather, grow, process and cook Australian Wild Foods. Ti Tree Press, Australia p 196 (As Planchonella australis) ; Coronel, R.E., 1982, Fruit Collections in the Philippines. IBPGR Newsletter p 10 (As Planchonella australis) ; Cribb, A.B. & J.W., 1976, Wild Food in Australia, Fontana. p 49 (As Planchonella australis) ; Elliot, W.R., & Jones, D.L., 1997, Encyclopedia of Australian Plants suitable for cultivation. Vol 7. Lothian. p 355 (As Planchonella australis) ; Hibbert, M., 2002, The Aussie Plant Finder 2002, Florilegium. p 236 (As Planchonella australis) ; Isaacs, J., 1987, Bush Food, Aboriginal Food and Herbal Medicine. Weldons. p 68 (As Planchonella australis) ; Jones D, L, 1986, Ornamental Rainforest Plants in Australia, Reed Books, p 238, 340 (As Planchonella australis) ; Lord, E.E., & Willis, J.H., 1999, Shrubs and Trees for Australian gardens. Lothian. p 20 (As Planchonella australis) ; Low, T., 1991, Wild Food Plants of Australia. Australian Nature FieldGuide, Angus & Robertson. p 90 (As Planchonella australis) ; Low, T., 1992, Bush Tucker. Australia´s Wild Food Harvest. Angus & Robertson. p 61 (As Planchonella australis) ; Lyle, S., 2006, Discovering fruit and nuts. Land Links. p 333 ; Nicholson, N & H., 1994, Australian Rainforest Plants 4, Terania Rainforest Publishing. NSW. p 55 (As Planchonella australis) ; Ratcliffe D & P., 1987, Australian Native Plants for Indoors. Little Hills press. p 116 (As Planchonella australis) ; Recher, P, 2001, Fruit Spirit Botanical Gardens Plant Index. www.nrg.com.au/~recher/ seedlist.html p 3 (As Planchonella australis) ; Williams, J.B., Harden, G.J., and McDonald, W.J.F., 1984, Trees and shrubs in rainforests of New South Wales and Southern Queensland. Univ. of New England, Armidale. p 92 (As Planchonella australis) ; Yallakool Reserve Plant List July 1, 2009 Off internet
Recherche de/pour :
- "Planchonella australis" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
- "Pomme noire" sur Google (pages, images et recettes) ;
- "Planchonella australis" sur Google (pages et
images) ;
TROPICOS (en anglais) ;
Tela Botanica ;
Pl@ntNet ;
Pl@ntUse ;
Espèces du même genre (Planchonella)
✖17 taxons
- Planchonella annamensis
- Planchonella arnhemica
- Planchonella australis (R.Br.) Pierre (Pomme noire)
- Planchonella chartacea
- Planchonella costata
- Planchonella duclitan
- Planchonella eerwah
- Planchonella endlicheri
- Planchonella euphlebia
- Planchonella grandifolia
- Planchonella grayana
- Planchonella laurifolia
- Planchonella lifuana
- Planchonella myrsinodendron
- Planchonella obovata
- Planchonella pohlmaniana
- Planchonella sp.
Espèces de la même famille (Sapotaceae)
✖50 taxons (sur 367)
- Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels (Arganier)
- Autranella congolensis
- Baillonella toxisperma Pierre (Beurre d'Orère)
- Beccariella brownlessiana
- Beccariella macrocarpa
- Beccariella papyracea
- Bumelia lanuginosa
- Bumelia lycioides
- Bumelia tenax
- Burckella banikiensis
- Burckella fijiensis
- Burckella macropoda
- Burckella majus
- Burckella obovata
- Burckella richii
- Burckella sorei
- Burckella sp megahilum
- Burckella thurstonii
- Chromolucuma rubiflora
- Chrysophyllum africanum A.DC. (Caïmitier africain)
- Chrysophyllum albidum G.Don (Caïmitier à fruit blanc)
- Chrysophyllum amazonicum
- Chrysophyllum arenarium
- Chrysophyllum argenteum Jacq.
- Chrysophyllum bangweolense
- Chrysophyllum boivinianum
- Chrysophyllum bombycinum
- Chrysophyllum brenesii
- Chrysophyllum cainito L. (Caïmitier)
- Chrysophyllum cuneifolium
- Chrysophyllum eximium
- Chrysophyllum flexuosum Mart.
- Chrysophyllum giganteum
- Chrysophyllum gonocarpum
- Chrysophyllum gorungosanum
- Chrysophyllum imperiale
- Chrysophyllum inornatum
- Chrysophyllum lacourtianum
- Chrysophyllum lucentifolium
- Chrysophyllum macoucou
- Chrysophyllum manaosense
- Chrysophyllum marginatum
- Chrysophyllum mexicanum
- Chrysophyllum michino H. B. & Kunth
- Chrysophyllum obovatum
- Chrysophyllum oliviforme L. (Satinleaf)
- Chrysophyllum ovale
- Chrysophyllum paranaense
- Chrysophyllum perpulchrum
- Chrysophyllum pomiferum
- ...