! Nouveau site ici !
Vita > Plantae > Magnoliophyta > Magnoliopsida > Polygonales >
Polygonaceae > Fagopyrum
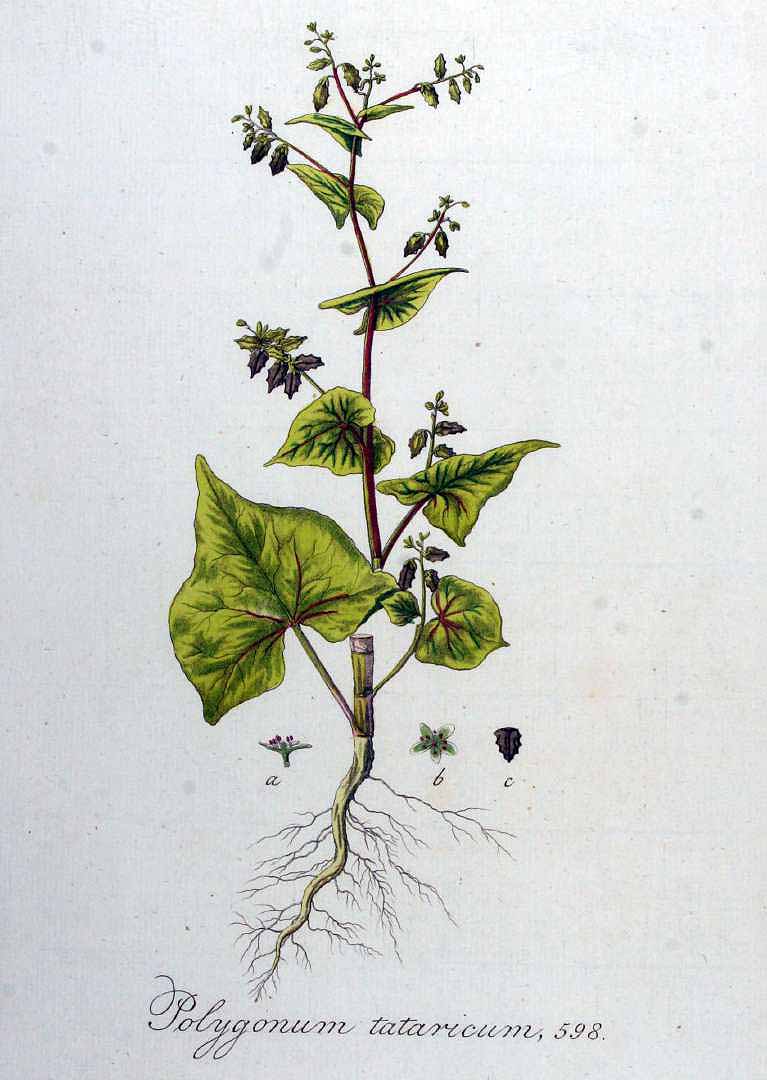
Fagopyrum tataricum
(Sarrasin de Tartarie)

 | *** - *
| *** - *
Vita > Plantae > Magnoliophyta > Magnoliopsida > Polygonales >
Polygonaceae > Fagopyrum
Fagopyrum tataricum
(Sarrasin de Tartarie)

Une herbe annuelle. Il atteint 100 cm de haut. Les feuilles supérieures ont de longues tiges. Les feuilles mesurent de 2,5 à 12 cm de long sur 2,5 à 11,5 cm de large. Ils sont de forme largement triangulaire... (traduction automatique)
→suite
⬀
Le  donne accès au menu
donne accès au menu (c'est votre point de repère) 😊 ;
En dessous vous avez la classification, à partir de la vie (Vita, premier rang) jusqu'à la classe au dessus de la plante, dont vous trouvez ensuite le nom scientifique/botanique (latin) puis le nom commun (français), le cas échéant ;
C'est aussi un lien vers la fiche complète (tout comme la ✖, en bas à droite, et le +, en dessous de la description) ;
Vient alors l'illustration (ou ce qui la remplace, en attendant), la comestibilité :
Et en bas
⬂

![Illustration Fagopyrum tataricum, Par Oeder, G.C., Flora Danica (1761-1861) Fl. Dan. vol. 15 (1852-1861) [tt. 2521-2700] t. 2649, via plantillustrations Illustration Fagopyrum tataricum, Par Oeder, G.C., Flora Danica (1761-1861) Fl. Dan. vol. 15 (1852-1861) [tt. 2521-2700] t. 2649, via plantillustrations](../inc/images/illustrations/fagopyrum_tataricum.jpg )



